Tutorial: Create environments with source control#
Feature availability
- Available on Enterprise.
- You need access to the n8n instance owner account or an admin account to set up source control, and to send work to and from Git.
This tutorial walks through the process of setting up environments end-to-end. You'll create two environments: development and production. It uses GitHub as the Git provider. The process is similar for other providers.
n8n has built its environments feature on top of Git, a version control software. You link an n8n instance to a Git branch, and use a push-pull pattern to move work between environments. You should have some understanding of environments and Git. If you need more information on these topics, refer to:
- Environments in n8n: the purpose of environments, and how they work in n8n.
- Git and n8n: Git concepts and source control in n8n.
Choose your source control pattern#
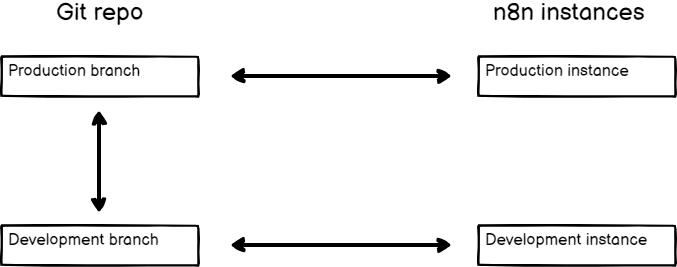
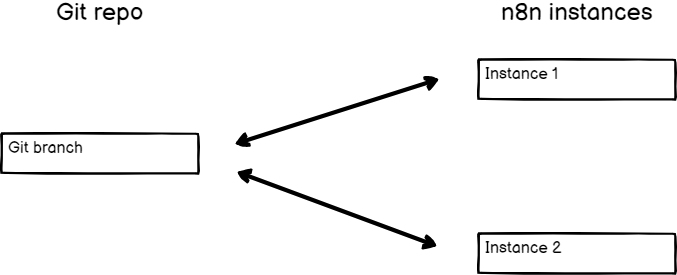
Before setting up source control and environments, you need to plan your environments, and how they relate to Git branches. n8n supports different Branch patterns. For environments, you need to choose between two patterns: multi-instance, multi-branch, or multi-instance, single-branch. This tutorial covers both patterns.
Recommendation: don't push and pull to the same n8n instance
You can push work from an instance to a branch, and pull to the same instance. n8n doesn't recommend this. To reduce the risk of merge conflicts and overwriting work, try to create a process where work goes in one direction: either to Git, or from Git, but not both.
Multiple instances, multiple branches#
The advantages of this pattern are:
- An added safety layer to prevent changes getting into your production environment by mistake. You have to do a pull request in GitHub to copy work between environments.
- It supports more than two instances.
The disadvantage is more manual steps to copy work between environments.
Multiple instances, one branch#
The advantage of this pattern is that work is instantly available to other environments when you push from one instance.
The disadvantages are:
- If you push by mistake, there is a risk the work will make it into your production instance. If you use a GitHub Action to automate pulls to production, you must either use the multi-instance, multi-branch pattern, or be careful to never push work that you don't want in production.
- Pushing and pulling to the same instance can cause data loss as changes are overridden when performing these actions. You should set up processes to ensure content flows in one direction.
Set up your repository#
Once you've chosen your pattern, you need to set up your GitHub repository.
- Create a new repository.
- Make sure the repository is private, unless you want your workflows, tags, and variable and credential stubs exposed to the internet.
- Create the new repository with a README so you can immediately create branches.
- Create one branch named
productionand another nameddevelopment. Refer to Creating and deleting branches within your repository for guidance.
- Make sure the repository is private, unless you want your workflows, tags, and variable and credential stubs exposed to the internet.
- Create the new repository with a README. This creates the
mainbranch, which you'll connect to.
Connect your n8n instances to your repository#
Create two n8n instances, one for development, one for production.
Configure Git in n8n#
- Go to Settings > Environments.
- In Git repository URL enter the SSH URL for your repository.
- n8n supports ED25519 and RSA public key algorithms. ED25519 is the default. Select RSA under SSH Key if your git host requires RSA.
- Copy the SSH key.
Set up a deploy key#
Set up SSH access by creating a deploy key for the repository using the SSH key from n8n. The key must have write access. Refer to GitHub | Managing deploy keys for guidance.
Connect n8n and configure your instance#
- In Settings > Environments in n8n, select Connect. n8n connects to your Git repository.
- Under Instance settings, choose which branch you want to use for the current n8n instance. Connect the production branch to the production instance, and the development branch to the development instance.
- Production instance only: select Protected instance to prevent users editing workflows in this instance.
- Select Save settings.
- In Settings > Environments in n8n, select Connect.
- Under Instance settings, select the main branch.
- Production instance only: select Protected instance to prevent users editing workflows in this instance.
- Select Save settings.
Push work from development#
In your development instance, create a few workflows, tags, variables, and credentials.
To push work to Git:
-
Select Push
 in the main menu.
in the main menu. -
In the Commit and push changes modal, select which workflows you want to push. n8n automatically pushes tags, and variable and credential stubs.
- Enter a commit message. This should be a one sentence description of the changes you're making.
- Select Commit and Push. n8n sends the work to Git, and displays a success message on completion.
Pull work to production#
Your work is now in GitHub. If you're using a multi-branch setup, it's on the development branch. If you chose the single-branch setup, it's on main.
- In GitHub, create a pull request to merge development into production.
- Merge the pull request.
- In your production instance, select Pull
 in the main menu.
in the main menu.
In your production instance, select Pull ![]() in the main menu.
in the main menu.
Optional: Use a GitHub Action to automate pulls#
If you want to avoid logging in to your production instance to pull, you can use a GitHub Action and the n8n API to automatically pull every time you push new work to your production or main branch.
A GitHub Action example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
Next steps#
Learn more about:
- Environments in n8n and Git and n8n
- Source control patterns
- Reusable Variables and Managing variables using the API when using source control.