Item linking concepts#
Each output item created by a node includes metadata that links them to the input item (or items) that the node used to generate them. This creates a chain of items that you can work back along to access previous items. This can be complicated to understand, especially if the node splits or merges data. You need to understand item linking when building your own programmatic nodes, or in some scenarios using the Code node.
This document provides a conceptual overview of this feature. For usage details, refer to:
- Item linking for node creators, for details on how to handle item linking when building a node.
- Item linking in the Code node, to learn how to handle item linking in the Code node.
- Item linking errors, to understand the errors you may encounter in the editor UI.
n8n's automatic item linking#
If a node doesn't control how to link input items to output items, n8n tries to guess how to link the items automatically:
- Single input, single output: the output links to the input.
- Single input, multiple outputs: all outputs link to that input.
- Multiple inputs and outputs:
- If you keep the input items, but change the order (or remove some but keep others), n8n can automatically add the correct linked item information.
- If the number of inputs and outputs is equal, n8n links the items in order. This means that output-1 links to input-1, output-2 to input-2, and so on.
- If the number isn't equal, or you create completely new items, n8n can't automatically link items.
If n8n can't link items automatically, and the node doesn't handle the item linking, n8n displays an error. Refer to Item linking errors for more information.
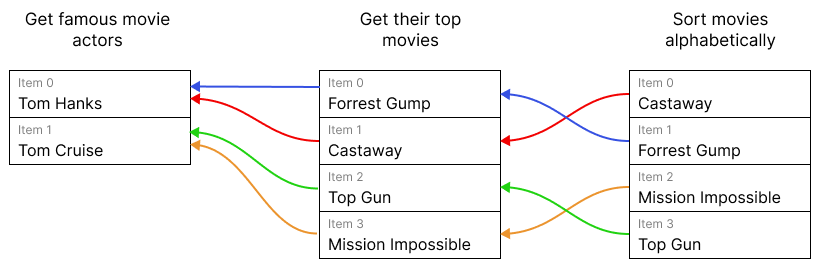
Item linking example#
In this example, it's possible for n8n to link an item in one node back several steps, despite the item order changing. This means the node that sorts movies alphabetically can access information about the linked item in the node that gets famous movie actors.
The methods for accessing linked items are different depending on whether you're using the UI, expressions, or the code node. Explore the following resources: